Last Updated: February 20, 2019
Description
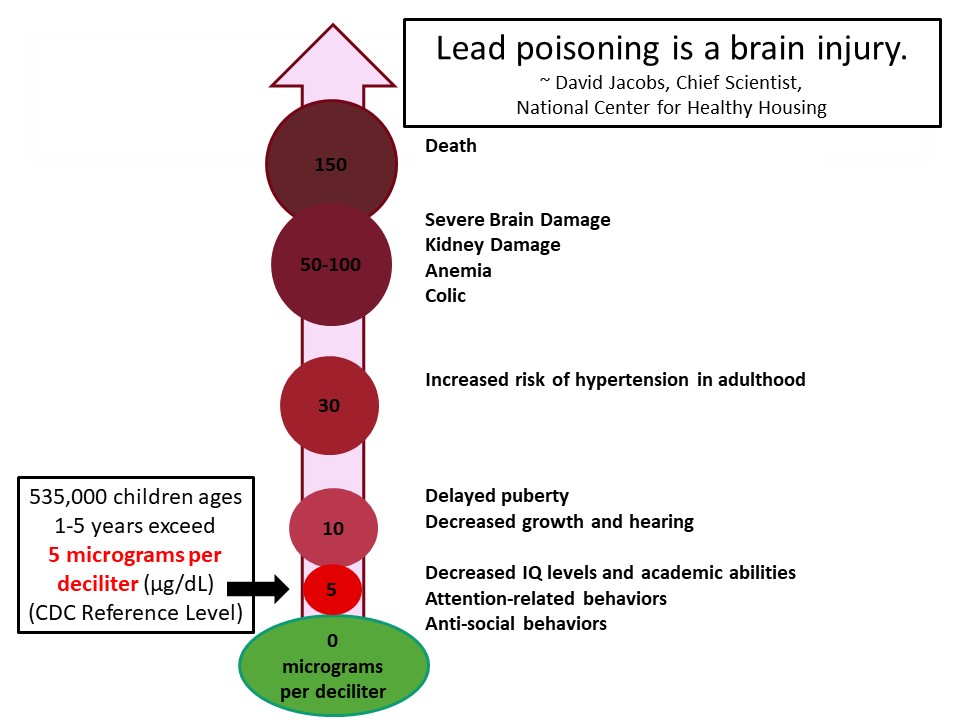
Lead: Blood Lead Levels
Image: Journal of Clinical Investigation, adapted from Bellinger and Bellinger 2006
Big idea: We are most concerned about the impacts of lead on young children and pregnant women.
Talking points:
- National data: 535,000 US children ages 1 to 5 years have BLLs high enough to damage their health
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) uses a reference level of 5 micrograms of lead per deciliter of blood (μg/dL) to identify children whose blood lead levels are much higher than most children’s levels and recommend initiation of public health actions. (The reference level, prior to 2016, was 10 μg/dL.)
- No safe blood lead level in children has been identified.
Sources:
Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry. Lead toxicity physiologic effects.
President’s Task Force on Environmental Health Risks and Safety Risks to Children, 2016
Categories: Lead